Remote Internet Experiments
Remote Lab includes real physics experiments that can be controlled from your web browser. Our remote experiments can be used absolutely free of charge and without any registration. You can always download the measured data to your computer for further processing and analysis.
Remote-LAB GymKT
We will present each remote (internet controlled) experiments created in our school on these pages. You can watch these experiments through the Internet, but also directly measure the real data. Remote experiments can be used as an experiment in multimedia-supported frontal teaching, but mainly thanks to their 24-hour availability as an experimental homework for students. They also find their unquestionable use in the so-called distance learning.
Remote-controlled experiments have many important advantages over traditional school experiments in traditional school laboratories or virtual simulations.


AVAILABILITY
Free access to the laboratory (anytime, anywhere), the experimenter does not need any physical tools, the experiment can be repeated several times.

SAFETY
There is no risk of injury when working with hazardous materials, even though users are working with real-time instrumentation.

MODERN CONCEPT
Increased student interest, time savings for teachers, fast graphical processing of readings, readings are real.
Our remote experiments
Our goal is to present experiments that are not quite common in the classroom or the preparation of which is otherwise too time consuming for a high quality design.
Temperature Dependence of Resistance of Metals and Semiconductors
Experiment 1 – VILI
(„Vilík“)
The task is focused on measuring the resistance of platinum sensor and thermistor at different temperatures and comparing their temperature dependence on electrical resistance.

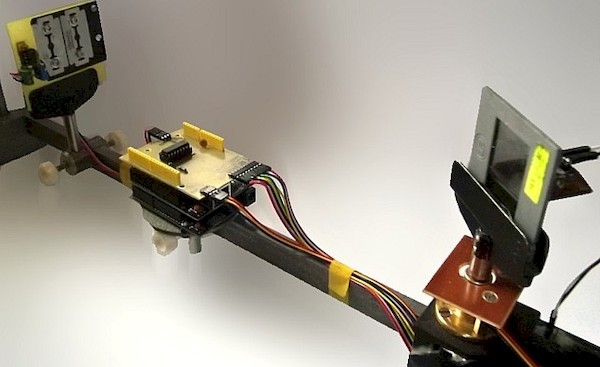
Determination of the Earth's magnetic field
Experiment 2 – NICoL
(„Nikolka“)
The determination of the horizontal component of the earths magnetic field is made by comparing the earths induction with the artificial induction induced by the so-called Helmholtz coils.
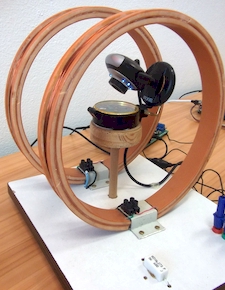
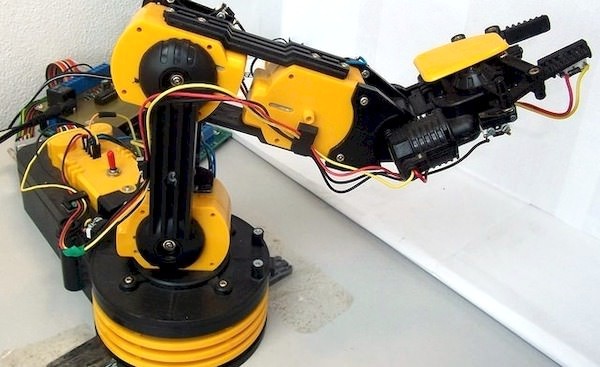
Robotic arm remote control
Experiment 3 – RAMBO
(„Rambík“)
The task is not the actual physical experiment where the measured result is important. In this role, you can "play" with the control of the robotic hand.
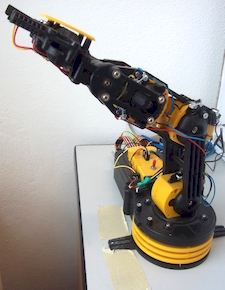
V-A Charakteristics of LED
(Determination of Planck constant)
Experiment 4 – CEcIL
(„Cecilka“)
The voltamper characteristics of the red, yellow, green, blue, and white LEDs can be compared in this experiment. The value of the Planck constant can also be determined.

Oscillations on the spring
(forced & damped oscillations)
Experiment 5 – IRMA
(„Irma“)
The experiment allows to study not only the real oscillation of the spring oscillator and the damped oscillation, but also the excited oscillation and the phenomenon called "resonance".

Basic features of the bipolar transistor
Experiment 6 – PaVEL
(„Pavlík“)
It is possible to measure the output and conversion characteristics in this task. In particular, the current gain can be determined for a common emitter configuration.

The purpose of the experiment is to measure the V-A characteristic of a classical light bulb, which is the first encounter of the students with so-called "non-linear loads".

Load characteristic of the source
Experiment 8 – ZaCHaRIAS
(„Zachariáš“)
The experiment allows you to measure the load characteristics of two commonly used electrochemical sources - alkaline and zinc-chloride batteries.

Study of diffraction phenomena
(Diffraction on a grating)
Experiment 9 – DiANE
(„Diana“)
The experiment is focuses on the study of the diffraction pattern on the optical grating. It is possible to determine the grating constant or the wavelength of the lasers used.

Solar cell load characteristics
Experiment 10 – DEVIL
(„Ďáblík“)
The experiment makes it possible to study the basic parameters of a solar cell as an energy source. It is possible to measure both the classical load characteristics and the power dependence on load.
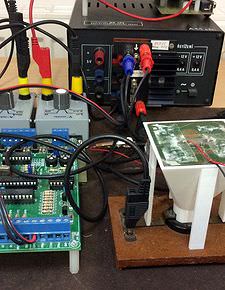
Radiation Absorption in Materials
Experiment 11 – AbRaHaM
(„Abrahám“)
The experiment demonstrates radiation shielding. It is possible to study the influence of different material thickness or different materials of the same thickness.

Weather Station
Experiment 12 – GENIE
(„Džin“)
Another project using the Arduino module with Ethernet Shield. This time the remote experiment concept is used as a simple weather station to monitor the conditions in our laboratory.

Remote Internet control of the K8055 board
App: K8055-MARIE
(„Maruška“)
K8055-MARIE is our application that allows remote control of the Velleman K8055(N) board. We are still developing this application, you can try the current version in the demos on this site.


- "We live in a society exquisitely dependent on science and technology, in which hardly anyone knows anything about science and technology. This is a clear recipe for disaster." (Carl Sagan)
- "Come on, damn it, let's try to avert this disaster!"
(Remote-LAB GymKT)